PTFE Conveyor Belts
Conveyor belts are made of fiberglass foil (PTFEPolytetrafluoroethylene, also known as Teflon, Hostaflon or Algoflon.), which is joined into an endless conveyor belt in different ways and with different types of joints.
In addition, the belts may have reinforced or stitched edges, overlapped joints, guides or be fitted with various other accessories.

Belts Construction

- Teflon bottom layer
- Glass or Kevlar fabric
- Teflon top layer
Belts Fields of Use
PTFE conveyor belts are designed for use in special applications where a highly heat-resistant, non-stick or hygienically clean surface is required.
They are most often used in packaging machines, in plastics processing, in vulcanization, on machine tools and in printing machines, in the food industry – e.g. in bakeries, chocolate factories, freezers, but also in the automotive industry and other industries.
Belts Joints
PTFE foils can be joined in endless conveyor belts in various ways and types of joints. We will be happy to advise you on the selection of the most suitable material for the conveyor belt and the method of its connection, or we will consult them with the manufacturer's technicians.
| Joint Type | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
Overlap Joint |
This is an overlapping joint. It is simple and applicable in cases where it is not crucial to have a flat surface. |
 |
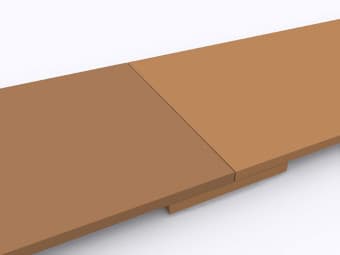
Butt Joint with Strap on Underside |
A butt joint with a strap on the underside is made by placing the two ends of the belt together and a strip of material is placed under the belt. All parts are then welded together to make the top surface smooth and even. |
 |
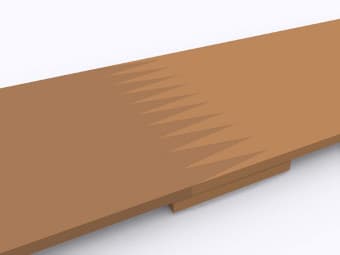
Finger Joint with Strap on Underside |
Finger joints with a strap on the underside are manufactured in a similar way to butt types, but offer less bending stress in the joint area. The joint offers improved stress and bending properties. |
 |
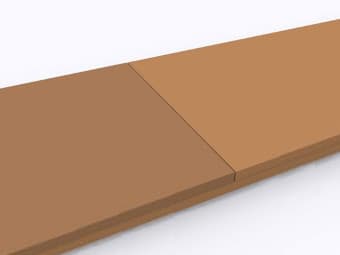
2-Ply Belts with Staggered Splice |
2-ply belts are constructed of two plies of PTFE coated fabrics, laminated together with staggered splices. This provides a smooth, continuous thickness along the entire belt length which guarantees a uniform seal in packaging and heat-sealing applications. This material combination results in higher strength and better overall flexibility. |
 |
Anker G Hook Clips |
Metal hooks are pressed into the ends of the belt, so that the belt can be joined into an endless one with a metal bar. It is possible to make sure that the hooks do not protrude above the surface of the belt. Suitable for belts with higher stress. |
 |
Anker A Hook Clips |
With round hooks. Metal hooks are pressed into the ends of the belt, so that the belt can be joined into an endless one with a metal bar. It is possible to make sure that the hooks do not protrude above the surface of the belt. Suitable for belts with higher stress. |
 |
Castellated Joint |
At both ends, loops of aramid or fiberglass foil are formed, which fit together and the belt can be joined in place with a plastic bar. Suitable for lighter joints, the spiral does not protrude above the surface of the belt and does not cause damage to the products. |
 |
Overlapping mechanical joints can also be made to protect the material being transported or to protect the joint itself. The cover is made of foil, which is welded to one edge of the belt and when joining the belt together it covers the entire mechanical joint.
Edge Reinforcement Types

The edges of the conveyor belts can be edged or reinforced with various materials to prevent damage to the belt, cracking of the edges.
The edges can be made of different materials, in some cases the edges can be stitched.
Reinforcement of the belt edges with a welded PTFE fabric is necessary in the following cases.
- In heavier operation, when it is necessary to protect the edge of the belt or to increase the tensile strength.
- When using mesh fabric for transport purposes (drying belts).
- When using side guides and stud guides.
It is recommended to use double-sided edge reinforcement to achieve proper operation with large belt widths.
Belts Guiding Types
In some cases, it is necessary to ensure the longitudinal guide of the belts. There are several ways to provide that. Each of them has its advantages and limitations.
| Guiding Type | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
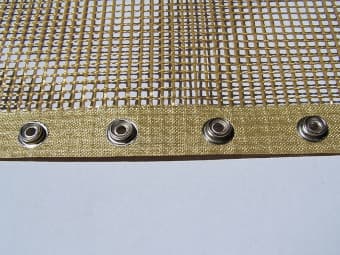
Metal Studs |
Guide with metal studs on the edge of the belt. A groove is made on the conveyor roller, into which the studs fit and ensure the guidance of the belt. Simple and cheap solution, suitable for belt speeds up to 20 m/min. The studs can be of different sizes and diameters. |
 |
Metal Eyelets |
Guide with metal eyelets on the edge of the belt. The metal eyelets are attached to the chain carriers with springs. |
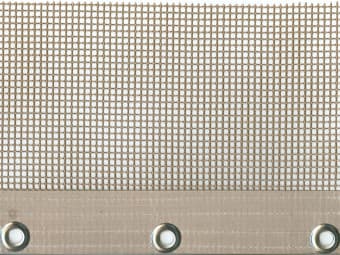 |
PTFE Studs with Pins |
PTFE guide pins are attached with studs to the reinforcement on the belt side. A groove is made on the conveyor roller, into which the studs fit and ensure the guidance of the belt. This guiding type is resistant up to 260 °C. |  |
Kevlar Cord |
Kevlar cord of various sizes is attached by stitching on the edge of the belt. It is an alternative to wedge guides for common types of conveyor belts. A groove is made on the conveyor roller, into which the cord fits and ensures the belt guide. |  |
Question about the Belts Category
Do not hesitate to contact us with any questions about products in this category.





